
Loading...
Disable Preloader

Dr. Dhanshree Salunkhe
Book Appointment
Antenatal vaccination
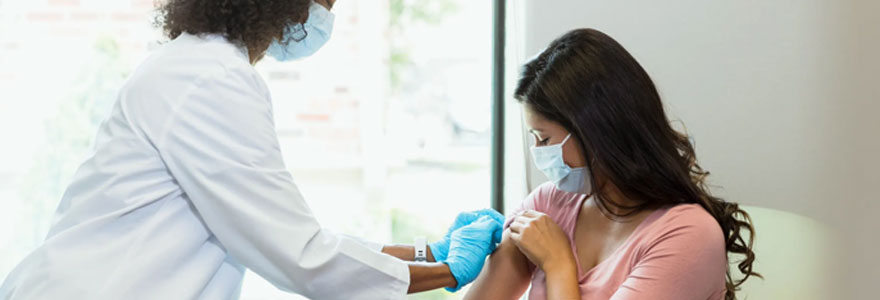
Antenatal vaccination, also known as prenatal vaccination or maternal immunization, refers to the administration of vaccines to pregnant women during their pregnancy to protect both the mother and the developing fetus from certain infections. This practice helps provide immunity to the baby in the first few months of life and ensures that both mother and child are less susceptible to specific diseases.
Advantages and Benefits:
- Protection for the Baby: Antenatal vaccination provides passive immunity to the developing fetus, helping to protect the baby during the first few months of life when they are too young to be vaccinated themselves.
- Reduced Risk of Complications: By receiving vaccines during pregnancy, the mother is less likely to contract certain diseases like influenza or pertussis, which can lead to complications, hospitalization, or even death.
- Healthy Pregnancy: Antenatal vaccination supports a healthier pregnancy by reducing the risk of infectious diseases that could harm the mother or the developing baby.
- Protection Beyond Birth: The immunity passed on to the baby can provide protection for several months, bridging the gap until the baby can receive their own vaccinations.
- Community Protection: Antenatal vaccination also contributes to community immunity, helping to reduce the spread of certain diseases within the community.
